Headache
Cases for Discussion
Case 1:
32 year old school teacher is referred for evaluation of headache.
She has had headaches since age15 mainly during her 'periods'. She experiences mood disturbance, irritability and depressive symptoms 2 days prior to her periods before the onset of headache. Either before or during her headache she sees some hazy spot from the center of her vision with shimmering light of different patterns spreading across her peripheral vision, followed by constriction of her visual field and this lasts for 20-30minutes.
Her headache is usually in the fronto-temporal area (one side or the other). It is throbbing / pounding in nature usually lasting 2-3 hours, at times whole day, especially during her menstruation. She has associated nausea and occasional vomiting. Bright light, sound and sometimes 'perfumes' worsen her headache.
Over the last 2 years severity and frequency of her headache worsened to 2-3 episodes of headache per week.
She is a heavy smoker. She is on birth control pills since last 2 years.
She has a family history of similar headache in her mother and her younger sister.
Recently, her 54 year old mother had a stroke.
Physical Examination: She is overweight (273 lbs): B.P is 140/85
No papilledema on Fundoscopc examination.
Her systemic and neurological examinations are otherwise normal.
Questions:
1. What are her visual symptoms called? Are they TIAs?
2. What is your diagnosis?
3. How do you treat her?
4. What non-pharmacological interventions are important in her?
5. When is it appropriate to order an Imaging study for headache?
6. What are the 'Red flags' (diagnostic alarms) in the evaluation of headache disorders?
Case 2:
35 year old bartender complains of sudden onset of severe headache since 1 hour.
He woke up in the middle of night with severe headache which peaked in intensity within 10 minutes and persisted. His pain is in right retro-orbital and temporal region and he describes it 'as if someone has thrust a hot poker in my eye'. He has associated excessive lacrimation, nasal congestion and rhinorrhea.
He had similar episodes of headache 3 months ago, 2-3 times per week and always waking him from his sleep but as not as severe as his current experience. Even those episodes of pain were always on the Right side. The episodes lasted for 4 weeks and then went away.
He is a smoker (I pack / per day) and drinks 3-4 beers every night.
Examination: Vitals stable
He is restless and does not want to lie down.
Partial ptosis and miosis noted in his Right eye on examination
Right eye is congested and he has rhinorrhea and flushing of the right side of his face. Rest of the examination is normal.
Questions:
1. What is his Ptosis and miosis in his Right eye due to?
2. What is your diagnosis?
3. What other investigations are necessary to confirm the diagnosis?
4. How do you treat him?
5. Is alcoholism the cause of his headache?
6. Is this a hereditary condition?
Case 3:
22 year old lady was referred for evaluation of headache associated with blurry vision since 4 weeks.
She used to have occasional 'stress related' headache 2-3 times a year and it is relieved by over the counter NSAIDs. She has gained about 60lbs in weight over the last 1 year since the birth of her last child. She is taking birth control pills since 1 year.
Since 3-4 weeks she started having persistent headache associated with 'rhythmic sound' in both ears when she bends forwards or lies down. Her headache was worse on lying down. She had noticed intermittent 'black out' in her left eye lasting a few minutes, at least 3 times in the last 2 weeks.
Since last one week she had noted 'double vision' while looking to the left.
She is a nonsmoker, does not drink alcohol or use illicit drugs.
Examination: Vitals Stable
She is overweight (Wt 292 lbs)
Systemic examination: Unremarkable
Neurological examination:
- Left eye abduction is limited and has diplopia on looking to Left
- Visual acuity is normal
- Visual field (on confrontation testing) is also normal
Fundoscopic examination: Shows an ominous finding. (See Fig 1)
Rest of her neurological examination is normal
Questions:
1. What are the findings on fundoscopic examination indicative of?
2. Why does she have diplopia on looking to Left?
3. What is your diagnosis?
4. List the investigations in the order of importance for establishing the diagnosis?
5. Which specialists referrals are needed?
7. How do you treat her?
8. What is the prognosis?
Look at Fundoscopic examination Picture (Fig. 1)

Case 4:
50 year old lady was brought to ER with acute onset of severe headache.
One month ago, she came to ER with sudden onset, severe headache associated with vomiting. She was discharged from ER after receiving injection of Ketorolac (Toradol) and Hydroxyzine (Vistaril). CT head did not reveal any acute abnormality then. Her headache resolved within the next 48 hours.
She presented to ER this time with 'worst headache of my life'. It started explosively, reaching its peak within a few seconds. She vomited once. She also complained of pain in the back of her neck and photophobia.
Physical Examination:
BP 140/90. HR 100/min, Afebrile, RR 20/minute
She was drowsy but easily arousable.
She had neck stiffness.
Bilateral LE weakness (3/ 5) with hyperreflexia in both LE and bilateral
Extensor plantar response noted bilaterally.
Rest of neurological examination was unremarkable
Questions:
1. What is the most likely diagnosis?
2. What is 'Thunderclap' headache? What are its important causes?
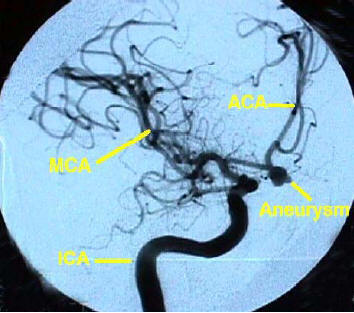
3. What does the CT head show in this lady? (Fig 2 below))
4 What are the causes of the abnormal finding on the CT Head?
5. How can we confirm the diagnosis of the cause of her problem?
6. What does this study show? (See Fig 3 below.)
7. What is the likely cause of her ER visit one month ago?
8. How do we manage this problem?
9. What are the serious neurologic complications of this disorder?
Look at CT head and Angiogram findings (Fig 2 and 3.)

Case 5:
71 year old retired school teacher was referred for evaluation of headache and transient episodes of blurring of vision.
Over last 3 months she had experienced intermittent Right temporal throbbing headache lasting 3- 4 hours, at least 2-3 times a week. Her headache had worsened over the last 2-3 weeks. It was now continuous 'burning' pain in right temporal region lasting all day. It became worse while lying on her right side, combing hair or washing her face. She also started experiencing pain her jaw and tongue while chewing food.
In the last week she had 3 episodes of transient blurring of vision in her right eye which lasted a few minutes. The day before, she had transient blurring of vision in her left eye also lasting 20 minutes.
She had dull aching pain in her shoulder and hip joints with some stiffness since one year. 'My arms and thighs hurt all the time'. She had lost 30lbs in the last 6 months.
Physical Examination:
Vital signs were stable and she was afebrile.
Slight tenderness noted over the Right temporal region
Movements of her hip and shoulder joints were painful.
No other systemic abnormalities were noted.
Neurological examination: unremarkable.
Questions:
1. What is her diagnosis?
-
-
What is the most worrisome symptoms associated with her headache?
-
What is the 'pain in her jaw and tongue when chewing food' called?
-
4. What is the most likely explanation for her musculoskeletal symptoms?
-
5. What is the most appropriate investigation? If it is 'normal' what is the
-
next best investigation to order?
-
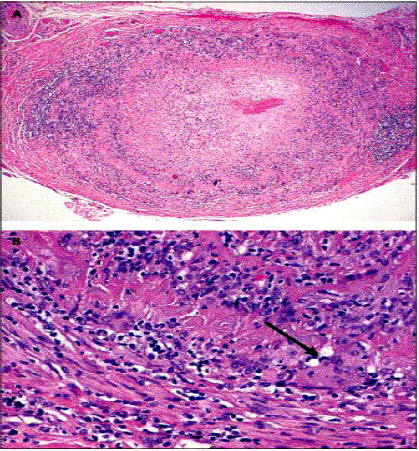
5. How do you confirm the diagnosis? What is its limitation? ( See Fig 6)
-
5. How do you treat her? Should you wait for confirmation of the
-
diagnosis before starting treatment?
-
Look at Biopsy findings (Fig 4)